ব্রিটিশ সমুদ্রপার অঞ্চলসমূহ
ব্রিটিশ সমুদ্রপার অঞ্চলসমূহ (ইংরেজি: British Overseas Territories, সংক্ষেপে BOTs) বা যুক্তরাজ্য সমুদ্রপার অঞ্চলসমূহ (ইংরেজি: United Kingdom Overseas Territories, সংক্ষেপে UKOTs) বলতে যুক্তরাজ্যের সাথে ঐতিহাসিক ও সাংবিধানিক সংযোগসহ ১৪টি নির্ভরশীল অঞ্চলকে বোঝায়। দাপ্তরিকভাবে যুক্তরাজ্যের অংশ না হলেও এই অঞ্চলগুলো যুক্তরাজ্যের সার্বভৌম ক্ষেত্রের অন্তর্গত।[১][২][৩] স্থায়ী বসতিযুক্ত অঞ্চলগুলোকে বিভিন্নরকম অভ্যন্তরীণ স্বায়ত্তশাসন দেওয়া হয়েছে, যেখানে যুক্তরাজ্য প্রতিরক্ষা, বৈদেশিক সম্পর্ক ও সুশাসনের জন্য দায়বদ্ধ।[৪][৫] যুক্তরাজ্য সরকারের এই দায়গুলোকে পররাষ্ট্র, কমনওয়েলথ ও উন্নয়ন দপ্তরের বিভিন্ন বিভাগে বরাদ্দ করা হয়েছে এবং এটি পরিবর্তিত হতে পারে। যুক্তরাজ্যের তিনটি সমুদ্রপার অঞ্চলে মূলত বা কেবল সামরিক কিংবা বৈজ্ঞানিক বসতি রয়েছে। অন্যান্য অঞ্চলে বেসামরিক জনগণ রয়েছে। ব্রিটিশ রাজশাসক যুক্তরাজ্যের ১৪টি সমুদ্রপার অঞ্চলের রাষ্ট্রপ্রধান।[৬]
ব্রিটিশ সমুদ্রপার অঞ্চলসমূহ British Overseas Territories | |
|---|---|
| সংগীত: "গড সেভ দ্য কিং" | |
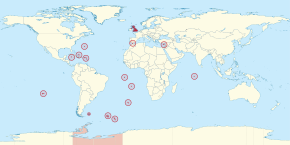 যুক্তরাজ্য ও ব্রিটিশ সমুদ্রপার অঞ্চলসমূহের মানচিত্র | |
| সার্বভৌম রাষ্ট্র | যুক্তরাজ্য |
| বৃহত্তম সমুদ্রপার অঞ্চল | ব্রিটিশ কুমেরু অঞ্চল |
| দাপ্তরিক ভাষা | ইংরেজি |
| বিশেষণ |
|
| সরকার | সাংবিধানিক রাজতন্ত্র |
• রাজা | তৃতীয় চার্লস |
| ঋষি সুনক | |
| ডেভিড ক্যামেরন | |
| ডেভিড রাটলি | |
| আয়তন | |
• মোট | ১৮,০১৫[ক] কিমি২ (৬,৯৫৬ মা২) |
| জনসংখ্যা | |
• ২০১৯ আনুমানিক | ২,৭২,২৫৬ |
| তারিখ বিন্যাস | দিন/মাস/বছর |
বর্তমান সমুদ্রপার অঞ্চলসমূহ
সম্পাদনাযুক্তরাজ্যের ১৪টি সমুদ্রপার অঞ্চলগুলো হলো নিম্নরূপ:[৭]
| পতাকা | প্রতীক | নাম | অবস্থান (মহাদেশ) |
নীতিবাক্য | আয়তন | জনসংখ্যা | রাজধানী | জিডিপি (স্বাভাবিক) |
মাথাপিছু জিডিপি (স্বাভাবিক) |
টীকা |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| আক্রোটিরি এবং ডেকিলিয়া (Akrotiri and Dhekelia) | সাইপ্রাস, ভূমধ্যসাগর, উত্তর আটলান্টিক মহাসাগর (ইউরোপ বা এশিয়া) |
২৫৫ বর্গকিলোমিটার (৯৮ বর্গমাইল)[৮] | স্থায়ী: ৭,৭০০ (সাইপ্রাসবাসী; আনুমানিক) অস্থায়ী: ৮,০০০ (ব্রিটিশ সামরিক কর্মকর্তা ও তাদের পরিবার; আনুমানিক) |
এপিস্কোপি ক্যান্টনমেন্ট | সামরিক ঘাঁটি ব্যতীত সম্পূর্ণ সার্বভৌমত্ব সাইপ্রাসের সাথে বিবাদিত। | |||||
| অ্যাঙ্গুইলা (Anguilla) |
ক্যারিবীয় অঞ্চল, উত্তর আটলান্টিক মহাসাগর (উত্তর আমেরিকা) |
"Unity, Strength and Endurance" (ইংরেজি: "ঐক্য, শক্তি ও সহনশীলতা") |
৯১ বর্গকিলোমিটার (৩৫.১ বর্গমাইল)[৯] | ১৪,৮৬৯ (২০১৯ সালের অনুমান)[১০] | দ্য ভ্যালি | $২৯৯ মিলিয়ন | $২০,৩০৭ | |||
| বারমুডা (Bermuda) |
উত্তর আটলান্টিক মহাসাগর (উত্তর আমেরিকা) |
"Quo fata ferunt" (লাতিন: "ভাগ্য যেথায় [আমাদের] বহন করে") |
৫৪ বর্গকিলোমিটার (২০.৮ বর্গমাইল)[১১] | ৬২,৫০৬ (২০১৯ সালের অনুমান)[১২] | হ্যামিলটন | $৬.৪৬৪ বিলিয়ন | $১,০২,৯৮৭ | |||
| ব্রিটিশ কুমেরু অঞ্চল (British Antarctic Territory) |
অ্যান্টার্কটিকা | "Research and discovery" ইংরেজি: "গবেষণা ও আবিষ্কার") | ১৭,০৯,৪০০ বর্গকিলোমিটার (৬,৬০,০০০ বর্গমাইল)[৯] | স্থায়ী: ০ অস্থায়ী: শীতকালে ৫০ জন, গ্রীষ্মকালে ৪০০ জনের বেশি (গবেষণা কর্মকর্তা)[১৩] |
রথেরা (মূল বৈজ্ঞানিক ঘাঁটি) | অ্যান্টার্কটিক চুক্তি ব্যবস্থার অন্তর্গত। | ||||
| ব্রিটিশ ভারত মহাসাগরীয় অঞ্চল (British Indian Ocean Territory) |
উত্তর ভারত মহাসাগর (আফ্রিকা বা এশিয়া) |
"In tutela nostra Limuria" (লাতিন; "লেমুরিয়া আমাদের অধীনস্থ") | ৬০ বর্গকিলোমিটার (২৩ বর্গমাইল)[১৪] | স্থায়ী: ০ অস্থায়ী: ৩,০০০ (যুক্তরাজ্য ও যুক্তরাষ্ট্রের সামরিক কর্মকর্তা; আনুমানিক)[১৫] |
নেভাল সাপোর্ট ফ্যাসিলিটি দিয়েগো গার্সিয়া (ঘাঁটি) | মরিশাস এই অঞ্চলকে দাবি করেছে। এতে চাগোস দ্বীপপুঞ্জের সাতটি অ্যাটল ও দিয়েগো গার্সিয়া দ্বীপ রয়েছে। | ||||
| ব্রিটিশ ভার্জিন দ্বীপপুঞ্জ (British Virgin Islands) |
ক্যারিবীয় অঞ্চল, উত্তর আটলান্টিক মহাসাগর (উত্তর আমেরিকা) |
"Vigilate" (লাতিন: "সতর্ক থাকুন") | ১৫৩ বর্গকিলোমিটার (৫৯ বর্গমাইল)[১৬] | ৩১,৭৫৮ (২০১৮ সালের জনশুমারি)[১৭] | রোড টাউন | $১.০৫ বিলিয়ন | $৪৮,৫১১ |
আরও দেখুন
সম্পাদনাটীকা
সম্পাদনা- ↑ ব্রিটিশ কুমেরু অঞ্চল ব্যতীত।
তথ্যসূত্র
সম্পাদনা- ↑ "Supporting the Overseas Territories"। UK Government। ৬ অক্টোবর ২০১৪ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ৮ নভেম্বর ২০১৪।
There are 14 Overseas Territories which retain a constitutional link with the UK. .... Most of the Territories are largely self-governing, each with its own constitution and its own government, which enacts local laws. Although the relationship is rooted in four centuries of shared history, the UK government's relationship with its Territories today is a modern one, based on mutual benefits and responsibilities. The foundations of this relationship are partnership, shared values and the right of the people of each territory to choose to freely choose whether to remain a British Overseas Territory or to seek an alternative future.
- ↑ "British Overseas Territories Law"। Hart Publishing। ২১ জুন ২০২০ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৯ জুন ২০২০।
Most, if not all, of these territories are likely to remain British for the foreseeable future, and many have agreed modern constitutional arrangements with the British Government.
- ↑ "United Kingdom Overseas Territories – Toponymic Information" (পিডিএফ)। Present Committee on Geographic Names। ১১ মে ২০২২ তারিখে মূল (পিডিএফ) থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ৭ জানুয়ারি ২০২৩।
- ↑ "Representing the Overseas Territories in the UK Parliament and Government"। UK Parliament (House of Commons Library)। UK Government। ৭ ফেব্রুয়ারি ২০২৩। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৪ জানুয়ারি ২০২৪।
All the Territories have a UK-appointed Governor, who generally holds responsibility for managing the Territory’s external affairs, defence and internal security like the police, and often the power to make or veto laws.......As a matter of constitutional law, the UK Parliament has unlimited power to legislate for the Territories. However, passing legislation for the Territories is rare.
- ↑ Leonard, Tom (১১ জুন ২০০৯)। "British anger over Bermuda decision to take Guantanamo detainees"। The Telegraph। ১০ জানুয়ারি ২০২২ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ২২ এপ্রিল ২০১৭।
We've underlined to the Bermuda Government that they should have consulted with the United Kingdom as to whether this falls within their competence or is a security issue, for which the Bermuda Government do not have delegated responsibility. We have made clear to the Bermuda Government the need for a security assessment, which we are now helping them to carry out, and we will decide on further steps as appropriate.
- ↑ "What is the British Constitution: The Primary Structures of the British State"। The Constitution Society। ৬ অক্টোবর ২০১৪ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৫ নভেম্বর ২০১৪।
The United Kingdom also manages a number of territories which, while mostly having their own forms of government, have the Queen as their head of state, and rely on the UK for defence and security, foreign affairs and representation at the international level. They do not form part of the UK, but have an ambiguous constitutional relationship with the UK.
- ↑ "Overseas Territories"। UK Overseas Territories Foreign & Commonwealth Office। ৫ আগস্ট ২০০২ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ৮ ডিসেম্বর ২০১০।
- ↑ "SBA Cyprus"। Jncc.gov.uk। ১৩ অক্টোবর ২০১০ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ৮ ডিসেম্বর ২০১০।
- ↑ ক খ "British Antarctic Territory"। Jncc.gov.uk। ১৪ ডিসেম্বর ২০১৩ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ৮ ডিসেম্বর ২০১০।
- ↑ "Anguilla Population 2019"। ১০ আগস্ট ২০১৯ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৮ আগস্ট ২০১৯।
- ↑ "record view | Surface area in km2"। UNdata। ৪ নভেম্বর ২০০৯। ২৬ মে ২০২৪ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ৮ ডিসেম্বর ২০১০।
- ↑ "Bermuda Population 2019"। World Population Review। ১৬ আগস্ট ২০১৯ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৮ আগস্ট ২০১৯।
- ↑ "British Antarctic Territory"। Commonwealth Secretariat। ৫ জুন ২০১১ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ৮ ডিসেম্বর ২০১০।
- ↑ "British Indian Ocean Territory"। JNCC। ১৩ অক্টোবর ২০১০ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ৮ ডিসেম্বর ২০১০।
- ↑ "Commonwealth Secretariat – British Indian Ocean Territory"। Thecommonwealth.org। ৫ জুন ২০১১ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ৮ ডিসেম্বর ২০১০।
- ↑ "British Virgin Islands (BVI)"। CIA World Factbook। ৯ জানুয়ারি ২০২১ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ১৪ আগস্ট ২০১৯।
- ↑ "British Virgin Islands (BVI)"। ১৩ অক্টোবর ২০১০। ১৩ অক্টোবর ২০১০ তারিখে মূল থেকে আর্কাইভ করা।
আরও পড়ুন
সম্পাদনা- Charles Cawley. Colonies in Conflict: The History of the British Overseas Territories (2015) 444pp.
- Harry Ritchie, The Last Pink Bits: Travels Through the Remnants of the British Empire (London: Hodder & Stoughton, 1997).
- Simon Winchester, Outposts: Journeys to the Surviving Relics of the British Empire (London & New York, 1985).
- George Drower, Britain's Dependent Territories (Dartmouth, 1992).
- George Drower, Overseas Territories Handbook (London: TSO, 1998).
- Ian Hendry and Susan Dickson, "British Overseas Territories Law" (London: Hart Publishing, 2011)
- Ben Fogle, The Teatime Islands: Adventures in Britain's Faraway Outposts (London: Michael Joseph, 2003).
- Bonham C. Richardson (১৬ জানুয়ারি ১৯৯২)। The Caribbean in the Wider World, 1492–1992। Cambridge University Press। আইএসবিএন 9780521359771। সংগ্রহের তারিখ ৮ ডিসেম্বর ২০১০।
বহিঃসংযোগ
সম্পাদনা- Foreign and Commonwealth Office – UK Overseas Territories (পররাষ্ট্র ও কমনওয়েলথ দপ্তর — যুক্তরাজ্য সমুদ্রপার অঞ্চলসমূহ)
- United Kingdom Overseas Territories Association (যুক্তরাজ্য সমুদ্রপার অঞ্চল অ্যাসোসিয়েশন)
- British Overseas Territories Act 2002 (ব্রিটিশ সমুদ্রপার অঞ্চলসমূহ আইন, ২০০২)
